Write to read-only memory
Code and constant variables are both read-only. Any change to the code or the constant variables during the runtime can incur segmentation faults.
Write to code
The following piece of code results in a segmentation fault, because it tries to change the code.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
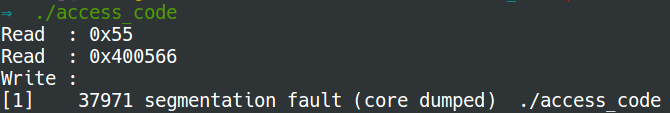
void *ptr = main;
unsigned char c = *((unsigned char *) ptr); //cast ptr to sth readable
printf("Read : 0x%x\n", c); // %x, Unsigned hexadecimal integer
printf("Read : %p\n", ptr); // %p, address stored in pointer(point address)
printf("Write : \n");
*((unsigned char *) ptr) = 0xff; //segmentation fault
printf("done\n");
return 0;
}
Write to constant variable
This sample code writes to a constant pointer.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
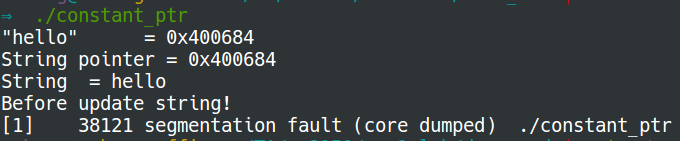
char *string = "hello"; //a pointer to a constant
printf("\"hello\" = %p\n", "hello");
printf("String pointer = %p\n", string);
printf("String = %s\n", string);
printf("Before update string!\n");
string[4] = '\0'; //segmentation fault
printf("After update string!\n");
printf("Go to %s\n", string);
return 0;
}